The rapid rise of remote work and digital transformation has fundamentally changed how businesses operate, driving an unprecedented demand for reliable and scalable data storage solutions. As organisations increasingly rely on cloud technology, the need for secure, efficient, and cost-effective storage has become paramount.
To put this growth into perspective, data stored in the cloud is projected to reach 100 zettabytes by 2025, accounting for the majority of global data storage. With nearly 10,978 data centres spread across the globe, cloud storage has emerged as a cornerstone for businesses aiming to enhance collaboration, scalability, and data security in today’s distributed work environment. According to Gartner, by 2027, cloud computing will become a key driver for business innovation and the common style of computing.
This blog explores Google Cloud Storage Pricing, evaluating its cost-effectiveness, best practices, and suitability for businesses of all sizes. Here are the key sections we’ll cover:
- What is Google Cloud Storage
- Key Features of Google Cloud Storage
- Types of Google Cloud Storage
- GCP Storage Pricing Tiers
- Why Google Cloud for Startups
- Tips to Optimize Costs on Google Cloud Storage Pricing
- Hidden Costs in Cloud Storage & How to Avoid Them
- Google Cloud Cost Comparison
- Industry-Specific Pricing Insights
- Will Google Cloud Have a Future?
- Conclusion
What is Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage is a highly scalable and reliable service that enables users to store their data on Google’s remote servers, ensuring accessibility anytime, anywhere. It leverages the performance and scalability of Google’s cloud infrastructure while integrating advanced security and sharing capabilities, making it an ideal solution for businesses and enterprises.
Operating as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Google Cloud Storage provides similar functionality to Amazon S3, offering robust tools for data storage and management. Unlike Google Drive, which is more consumer-focused, Google Cloud Storage is designed specifically for enterprises, accommodating large-scale data requirements and business-critical operations.
One of its distinguishing features is its multi-regional architecture, which allows businesses to store and replicate their data across different regions, ensuring 99.95% availability. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that require low-latency access to their data or need to comply with strict data residency regulations.
Another lesser-known fact is that Google Cloud Storage integrates seamlessly with Google’s machine learning tools, enabling users to run advanced analytics directly on stored data. For instance, businesses can leverage Google’s AI services, such as AutoML, to derive insights from their data without transferring it to external systems.
This service also enables businesses to securely store unstructured data, such as backups, media files, and analytics data, while supporting seamless data retrieval and sharing. Its scalability allows companies to grow their storage needs dynamically without compromising on performance or security, making it a preferred choice for organizations of all sizes.
Key Features of Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage is built to provide businesses with secure, high-performance, and cost-efficient cloud storage. Here are some of its standout features:
- High Availability: Multi-regional and regional storage ensures 99.95% uptime, improving data redundancy and accessibility across different locations.
- Industry-Leading Durability: Data is replicated across multiple locations, achieving 99.999999999% (11 9s) durability, significantly reducing the risk of data loss.
- Scalability & Performance: Capable of handling exabyte-scale storage with low-latency, high-throughput workloads, making it ideal for AI, analytics, and media applications.
- Advanced Security: Built-in encryption at rest and in transit, coupled with Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Object Versioning, ensures secure and controlled access.
- Automated Data Lifecycle Management: Businesses can set lifecycle policies to move or delete older data automatically, reducing unnecessary storage costs.
- Seamless Google Cloud Integration: Works effortlessly with BigQuery, Vertex AI, and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) to support advanced analytics, AI, and real-time data processing.
By leveraging these features, businesses can enhance storage efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain top-tier security.
Types of Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage offers four distinct storage classes, each catering to different business needs based on data access frequency, performance, and cost efficiency.
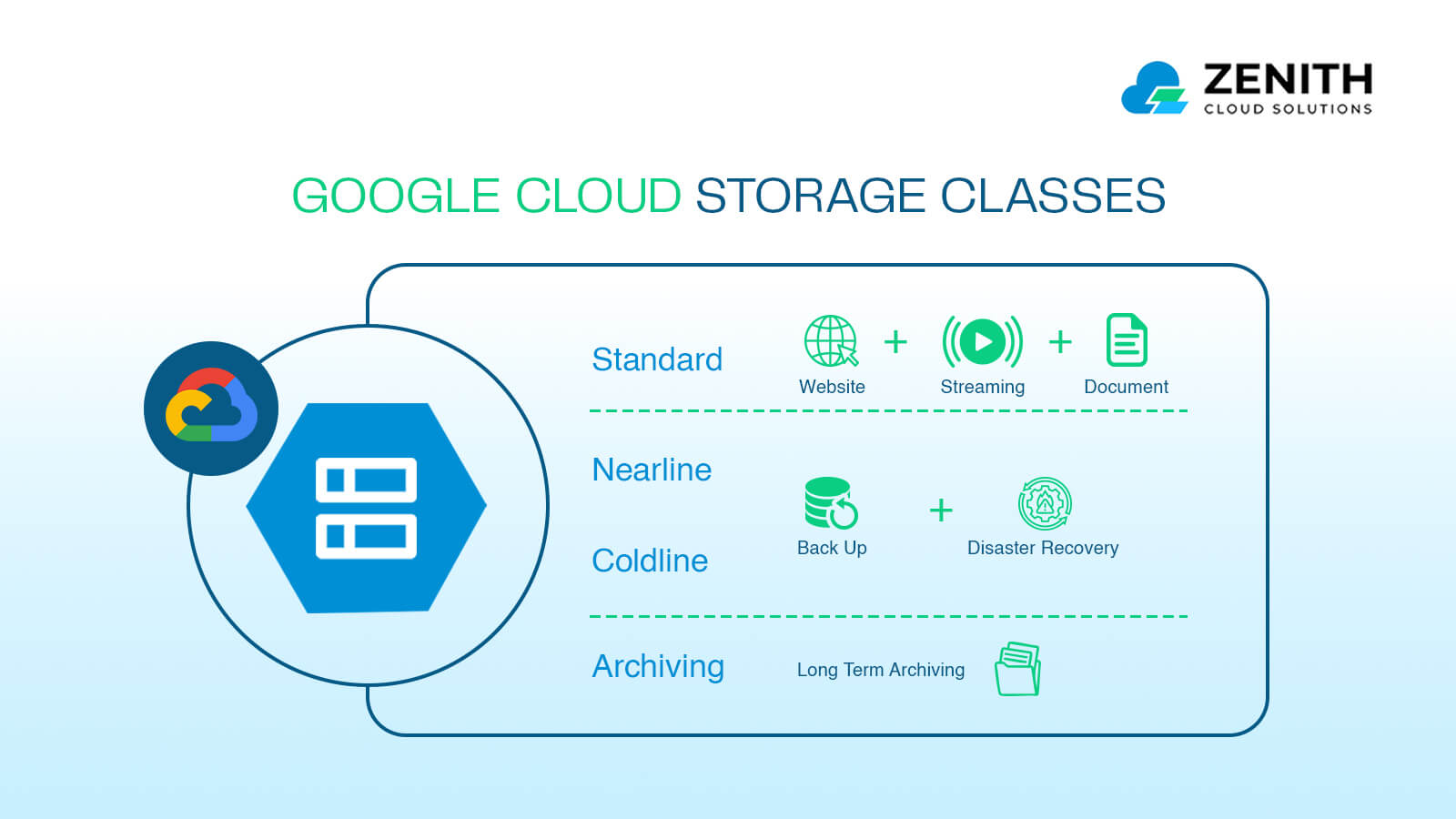
- Standard Storage: Standard Storage is best suited for businesses requiring frequent access to their data with minimal latency. This class is ideal for active workloads, such as hosting websites, serving real-time applications, and supporting high-traffic transactional data. It ensures rapid data retrieval, making it perfect for businesses where performance is a priority.
- Nearline Storage: Nearline Storage is designed for data that is accessed less frequently, typically once a month or less. This option is cost-effective for backup solutions, disaster recovery, and archiving. While retrieval costs are higher than Standard Storage, it offers a balance between affordability and accessibility, making it a great choice for businesses looking to optimize storage expenses.
- Coldline Storage: Coldline Storage caters to long-term archival needs, offering even lower storage costs for data that is accessed once a year or less. It is commonly used for compliance records, historical datasets, and infrequently accessed analytics data. While it offers significant cost savings, retrieval costs and latency are higher, making it suitable for businesses that prioritize storage over accessibility.
- Archive Storage: Archive Storage is the most budget-friendly option, designed for data that requires multi-year retention with little to no retrieval. This class is ideal for regulatory compliance, legal records, and other long-term storage needs where businesses need to store large volumes of data at minimal costs. Since retrieval times are longer, Archive Storage is best used for data that is rarely, if ever, accessed.
By selecting the appropriate storage class, businesses can effectively manage their cloud storage costs while ensuring that data remains secure and available as needed.
GCP Storage Pricing Tiers
Google Cloud Storage offers a tiered pricing model to help businesses optimize costs based on how frequently data is accessed. These storage classes balance cost and performance, ensuring businesses only pay for what they need.
| Storage Tier | Access Frequency | Pricing | Best For |
| Standard Storage | Frequent | Highest per GB | Active workloads, websites, streaming |
| Nearline Storage | Once a month | Lower than Standard | Backups, archives, disaster recovery |
| Coldline Storage | Once a year or less | Even lower | Compliance storage, historical records |
| Archive Storage | Rarely accessed | Lowest | Long-term retention, regulatory archives |
Each storage class balances cost and accessibility, allowing businesses to align their data strategy with performance and budget needs. GCP’s pricing tiers provide flexibility, allowing businesses to choose the right balance between cost and accessibility based on their data storage needs.
Why Google Cloud for Startups
Startups often face the challenge of scaling their infrastructure while managing costs effectively. Google Cloud Storage Pricing provides a tailored approach for startups, offering flexible pricing, technical support, and cloud credits that help businesses scale faster and smarter. Eligible startups can receive up to $200,000 in cloud credits, with AI-focused startups qualifying for up to $350,000.
In addition to cost savings, the Google Cloud Pricing Calculator allows startups to estimate and manage their cloud expenses in real time. Seamless integration with AI and machine learning tools enables startups to innovate without the burden of heavy infrastructure investments. Many high-growth startups, such as Snapchat and Evernote, have leveraged Google Cloud to enhance their operational efficiency. For instance, Snapchat migrated its services to Google Cloud to improve its global reach and service performance, while Evernote improved its data security and storage efficiency by adopting GCP Storage Pricing Tiers.
Google Cloud’s scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness make it an attractive choice for startups aiming to focus on growth and innovation without worrying about backend infrastructure. With a global network and industry-leading AI capabilities, Google Cloud Cost Comparison helps startups find the most affordable cloud storage options while staying competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Tips to Optimize Google Cloud Storage Pricing
Managing cloud storage efficiently can lead to significant cost savings. Here are some practical strategies businesses can implement:
- Choose the Right Storage Class: Move less frequently accessed data to Nearline, Coldline, or Archive Storage to reduce costs.
- Implement Lifecycle Policies: Automate data retention to delete or move old files to lower-cost storage tiers.
- Compress & Deduplicate Data: Use data compression and eliminate redundant files to save storage costs.
- Monitor & Optimize Data Transfers: Avoid excessive inter-region data transfers to reduce unexpected network charges.
- Take Advantage of Committed Use Discounts (CUDs): Leverage sustained-use and committed-use discounts to lower costs.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can optimize their cloud storage usage and reduce unnecessary expenses.
Hidden Costs in Cloud Storage & How to Avoid Them
While cloud storage is often marketed as a cost-effective solution, businesses frequently encounter hidden costs that can drive up expenses. Understanding and mitigating these costs is crucial for long-term cloud efficiency.
1. Data Egress and Transfer Costs
- Moving data between regions or out of Google Cloud incurs additional costs.
- Large-scale inter-region transfers can lead to unpredictable expenses.
- Optimization Tip: Keep data within the same region where possible and use Cloud CDN to reduce egress costs.
2. Retrieval Costs for Coldline & Archive Storage
- While Coldline and Archive Storage have low storage fees, retrieving data comes at a price.
- Accessing archived data can cost significantly more than storing it.
- Optimization Tip: Store only truly long-term data in Archive Storage and regularly review data lifecycle policies.
3. API & Request-Based Charges
- Frequent GET, PUT, and DELETE requests to Cloud Storage generate per-operation costs.
- Workloads involving millions of small file operations may incur substantial expenses.
- Optimization Tip: Batch operations and minimize unnecessary API calls.
4. Excessive Object Versioning
- Enabling Object Versioning prevents accidental deletion but increases storage costs.
- Older versions of files accumulate over time and inflate storage bills.
- Optimization Tip: Implement lifecycle rules to auto-delete outdated versions.
Understanding these hidden costs enables businesses to fine-tune their cloud storage strategy and avoid unexpected bills.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have unique data storage requirements, influencing their cost strategies on Google Cloud. Businesses in finance, healthcare, media, and AI leverage Google Cloud Storage for secure, scalable, and cost-effective solutions tailored to their operational needs.
Finance & Banking: Financial institutions prioritize secure, compliant storage for transaction records. Coldline Storage is frequently used for regulatory audits, while regional policies help maintain data sovereignty.
Healthcare & Life Sciences: Hospitals and research facilities store large datasets like medical imaging and patient records. Nearline Storage reduces costs by optimizing access for medical history retrieval.
Media & Entertainment: Video-heavy industries demand fast, low-latency access to large files. Multi-region Standard Storage enables real-time media access, while Nearline Storage manages ageing content.
Retail & eCommerce: Online retailers store high-volume transactional data. Standard Storage supports active databases, while Coldline Storage archives historical sales data for future insights.
By understanding industry-specific cost strategies, businesses can optimize their storage investments while ensuring compliance, efficiency, and scalability.
Will Google Cloud Have a Future?
Google Cloud has been consistently expanding its capabilities, investing in AI-driven innovations, sustainability, and enterprise-grade security. With businesses increasingly migrating to cloud-based solutions, Google Cloud is poised to play a significant role in the future of enterprise cloud storage and computing.
The platform’s continued focus on AI, machine learning, sustainability, and security ensures that it remains a competitive force. As cloud adoption grows and hybrid cloud solutions become more prevalent, Google Cloud will likely expand its enterprise offerings and industry partnerships to meet evolving business needs.
Conclusion
Selecting the right cloud platform is crucial for optimizing storage, performance, and cost efficiency. Google Cloud Storage provides a compelling solution for businesses looking to leverage scalability, security, and AI-driven analytics in their cloud strategy.
For businesses evaluating their cloud storage needs, Zenith Cloud Solutions offers expert consultation and migration services, helping enterprises seamlessly transition to cost-effective cloud environments.
Ready to future-proof your cloud storage? Get in touch with our experts today.

